BME690 Environmental Sensor
Product Description
Featuring one of the most advanced sensors in Bosch’s lineup, the BME690 Breakout Board adds air quality measurement on top of environmental (temperature, humidity, and pressure) sensing. With features such as Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), Volatile Sulfur Compounds (VSCs), and other gases, the BME690 provides an excellent upgrade to the BME688, especially for high condensation environments. Accuracy and applications can be further fine-tuned using Bosch’s BME AI-Studio to tune the BME690.
Key Features
- Four-in-One Sensor: Measures gas, humidity, pressure, and temperature
- Temperature measurement range: -40 to +85°C with ±0.5°C accuracy (0-65°C)
- Humidity measurement range: 0 to 100% RH with ±3% RH accuracy
- Pressure measurement range: 300 to 1100 hPa with ±0.5 hPa accuracy
- Gas sensor capabilities: Detects VOCs, volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs), CO, and H2
- Gas resistance range: 10 kΩ to 10 MΩ with variable resolution
- Ultra-low power consumption: 0.11 µA in sleep mode
- Digital interfaces: I²C (up to 3.4 MHz) and SPI (up to 10 MHz) communication
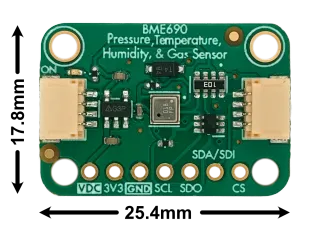
- Compact size: 25mm x 18mm package
- Operating voltage: 3.3V - 5V (VDD)
- 3.3V-5V logic levels
- Lead-Free
The BME690 is built on Bosch Sensortec’s proven environmental sensing technology and provides high-performance sensing with exceptional accuracy across its full operating range.
Includes an onboard LED that lights up when power is connected.


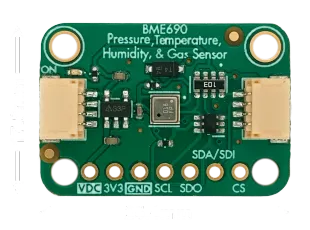
Pinout


| Pin | I/O | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VDC | I | 5V or 3.3V supply voltage matching communication logic level. |
| 3V3 | O | 3.3V output from 5V to 3.3V power regulator (100mA max). |
| GND | - | Ground |
| SCL | I | I²C Clock / SPI Clock |
| SDO | O | SPI Data Output (MISO) / I²C Address LSB (selects between 0x76 and 0x77) |
| SDA/SDI | I/O | I²C Data / SPI Data Input (MOSI) |
| CS | I | Chip Select (SPI mode - active low) |
Voltage Compatibility
The BME-690 Breakout Board can operate with both a 3.3V or a 5V supply on pin VDC. Logic levels should match supply voltage for proper operation.
Communication Interfaces
I²C Communication
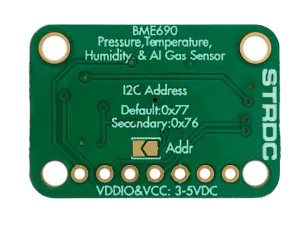
The BME690 supports I²C communication with two possible addresses, which can be selected either through the SDO pin or by soldering the Addr jumper.
- 0x76 (default when Addr jumper is open, SDO high or not connected)
- 0x77 (when Addr jumper is closed, SDO low)
The I²C interface supports standard (100 kHz), fast (400 kHz), and high-speed modes up to 3.4 MHz. Pull-up resistors are included on both SCL and SDA lines.
SPI Communication
For SPI communication, the BME690 supports 4-wire SPI mode:
- SCL: Serial Clock
- SDI: Serial Data Input (MOSI)
- SDO: Serial Data Output (MISO)
- CS: Chip Select (active low)
SPI clock frequencies up to 10 MHz are supported.
Power Modes
The BME690 is designed for power-efficient operation, featuring multiple modes to optimize energy use:
| Mode | Average Current | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep Mode | 0.11 µA | The sensor is inactive, consuming minimal power until a wake-up signal is received. Ideal for ultra-low-power applications. |
| Ultra-Low Power | 0.05 mA | Periodic sensor operation with minimal power draw. Suitable for applications requiring infrequent measurements. |
| Low Power | 0.5 mA | Optimized for power-efficient continuous monitoring while maintaining reasonable update rates. |
| Standard Gas Scan | 3.1 mA | Gas scanning mode optimized for air quality detection. |
| Continuous Mode | 12 mA | Provides the highest measurement frequency and fastest response times, best for real-time monitoring applications. |
Gas Sensing Capabilities
Detectable Gases
- VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds): Common indoor air pollutants
- VSCs (Volatile Sulfur Compounds): Odor-causing compounds
- CO (Carbon Monoxide): Dangerous combustion byproduct
- H2 (Hydrogen): Industrial gas detection
Gas Sensor Operation
The gas sensor operates by measuring the resistance of a heated metal oxide semiconductor. Different gases cause predictable changes in resistance, allowing for gas identification and concentration estimation.
Software Libraries and Examples
Arduino Libraries
Adafruit BME680 Library (Compatible)
While specifically designed for BME680, this library is compatible with BME690:
- Installation: Available through Arduino Library Manager
- Repository: Adafruit BME680 Library
- Features: Easy-to-use API, supports both I²C and SPI, includes basic gas sensing
Bosch BSEC Arduino Library (Compatible)
Designed for BME680, but compatible with BME690:
- Installation: Available through Arduino Library Manager
- Repository: Bosch BSEC Library
- Features: Easy-to-use API, supports I²C, advanced gas sensing examples
Platform Support
- Arduino: Compatible with BME680 libraries (requires level shifter)
- Raspberry Pi: Python libraries available via Adafruit CircuitPython
- ESP32/ESP8266: Compatible with Arduino libraries
- STM32: HAL libraries and CUBE support
BME AI-Studio
BME AI-Studio is Bosch Sensortec’s advanced software platform for developing AI-powered gas sensing applications with the BME690. This powerful tool enables users to create custom gas detection algorithms and train machine learning models for specific applications.
Key Features of BME AI-Studio
Machine Learning Integration
- Custom Model Training: Train models to recognize specific gas signatures
- Pattern Recognition: Identify complex gas patterns and environmental conditions
- Real-time Classification: Deploy trained models for real-time gas classification
Data Collection and Analysis
- Sensor Data Logging: Collect and analyze sensor data over time
- Environmental Profiling: Create baseline profiles for different environments
- Gas Signature Database: Build libraries of known gas signatures
Application Development
- Algorithm Development: Create custom algorithms for specific use cases
- Model Optimization: Optimize models for power consumption and accuracy
- Deployment Tools: Deploy trained models to BME690-based devices
Getting Started with BME AI-Studio
For documentation and information on the BME AI-Studio go to Bosch’s documentation here: BME AI-Studio
Helpful Notes
- Ensure proper calibration for accurate gas sensing results using BME AI-Studio
- The gas sensor is sensitive to environmental changes - ensure proper ventilation for stable readings
- Allow adequate warm-up time for the gas sensor (20-30 minutes for full accuracy)
- Protect from condensation - while the sensor can handle high humidity, water droplets can affect accuracy
- Use appropriate filtering for gas measurements in noisy environments
- Consider power management - gas sensing modes consume significantly more power than environmental sensing
Datasheets and Documentation
Schematic:
Chip Info and Product Datasheets:
Store Page:
FAQ
Q: What’s the difference between BME690 and BME680/BME688?
A: The BME690 is the next generation of Bosch’s environmental sensors, offering improved gas sensing accuracy, lower power consumption, and enhanced AI capabilities compared to the BME680. Compared to the BME688, the BME690 provides additional gas sensing capabilities and better integration with AI-Studio.
Q: How accurate are the gas readings?
A: Gas sensing accuracy depends on calibration, environmental conditions, and the specific gases being detected. The BME690 provides relative gas resistance measurements that can be calibrated for specific applications using BME AI-Studio.
Q: Can I use multiple BME690 sensors on the same I²C bus?
A: Yes, the BME690 supports two I²C addresses (0x76 and 0x77) by controlling the SDO pin state. This allows up to two sensors on the same I²C bus.
Q: How long does the gas sensor take to warm up?
A: The gas sensor typically requires 20-30 minutes to fully stabilize after power-on. For quick measurements, a 2-3 minute warm-up provides reasonable accuracy.
Q: Is the BME690 suitable for outdoor weather monitoring?
A: Yes, the BME690 can be used for outdoor applications, but the gas sensor should be protected from direct exposure to rain and extreme conditions. Consider using appropriate enclosures for outdoor deployments.
Q: How do I calibrate the gas sensor for my specific application?
A: Use BME AI-Studio to collect baseline data in your target environment and train custom models for your specific gas detection requirements. This provides much better accuracy than generic calibration.
Q: What causes unstable gas readings?
A: Common causes include:
- Insufficient warm-up time
- Temperature fluctuations affecting the heated sensor
- Air currents disrupting the measurement
- Contamination of the sensor surface
- Operating outside recommended environmental conditions

